KINGREAL UNIVERSAL IND., LTD
Phone
+86-13702855825| 1 | What is Overmolding? |
| 2 | Process of Overmolding |
| 3 | Advantages of Overmolding |
| 4 | Applications of Overmodling |
1.What is Overmolding?
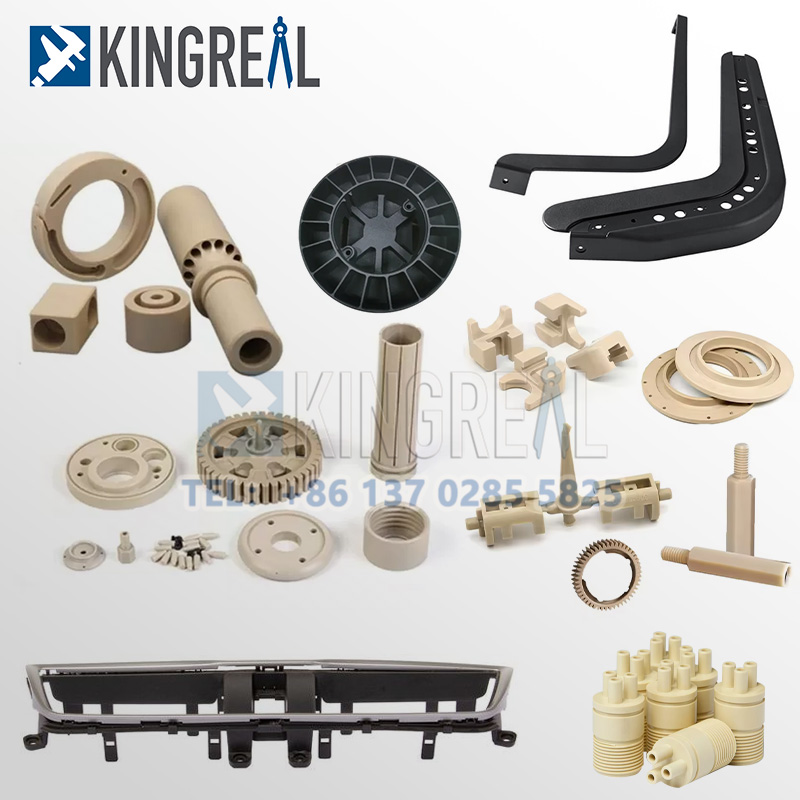
| Overmolding refers to the fastest, multi-step process of molding a layer of polymer over a substrate part using TPU injection molding methods. It usually represents the mechanical entanglement of polymer molecules. Usually, it is an injection molding process. The substrate part (the toughest part) is usually made of plastic and made by the plastic overmolding process. From toothbrush manufacturing to vibration reduction, and critical internal durable and elastic parts in automobiles and aerospace, the overmolding of small-size parts has received great attention. The process is carried out by chemical or physical interlocking. |  |
2.Process of Overmolding
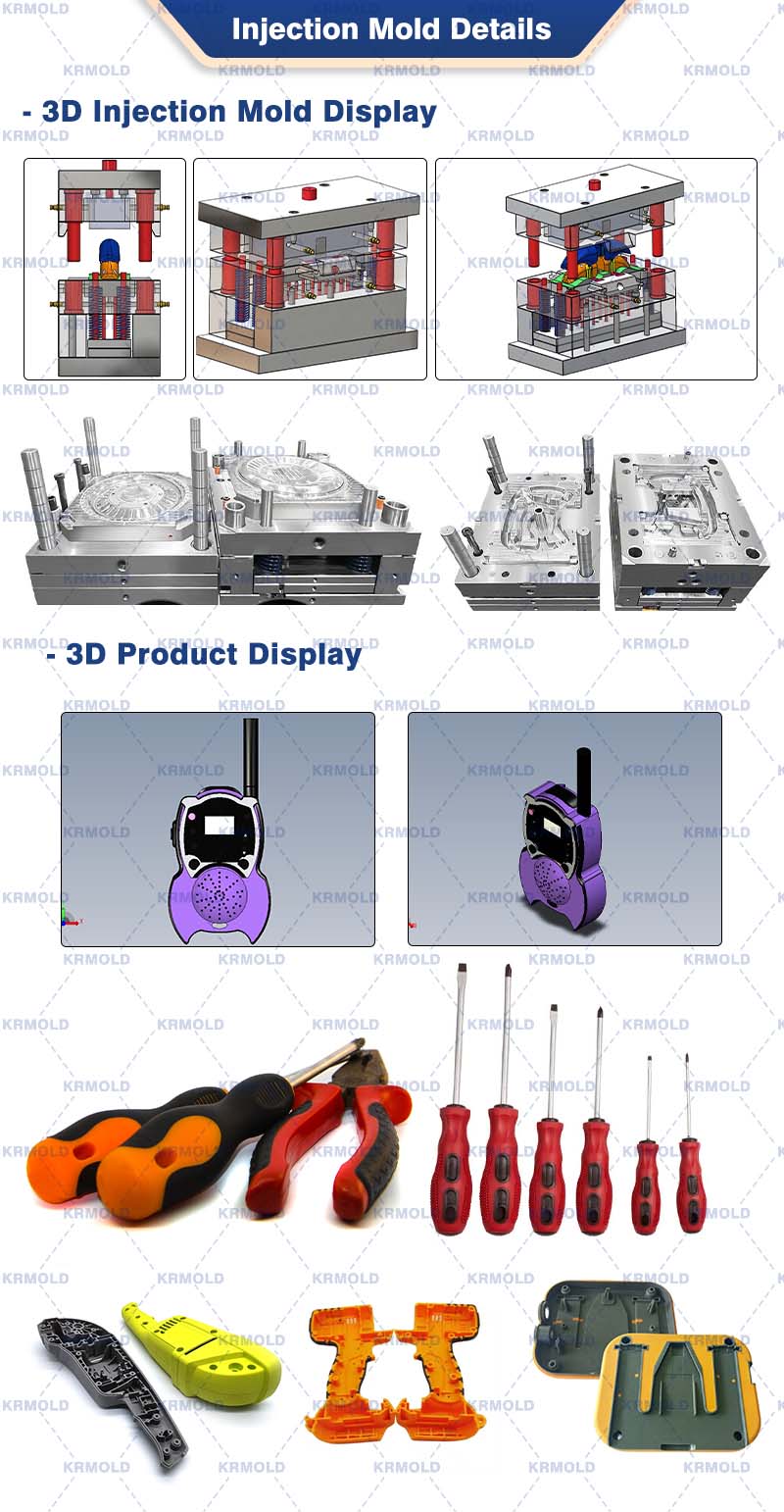
The first stage in the overmolding process is the design and creation of molds and tools. This entails developing a thorough design of the component and choosing the right materials and process settings. Tools and molds are then made to generate the specified components.
Once the mold and tooling are finished, the injection molding machine is ready for plastic overmolding. This includes setting the process parameters, installing the mold in the machine, and checking all needed supplies and tools are in place.
In some instances a premolding process may be necessary before the overmolding one starts. This might call for either inserting premolded parts into the mold or injecting molding of discrete components.
The first substance is injected into the mold to kick the plastic overmolding process. Injected into the mold, the substance is heated under pressure, filling the cavity and taking the shape of the component.
Overmolding is the process of injecting a second substance over the first after the first has been injected and cooled to a specific temperature. Usually injected at a lower temperature and pressure, the second material helps to protect the first substance from damage.
Once the plastic overmolding procedure is finished, the mold cools and the component is ejected from it. The component is then checked and completed as necessary.

3. Advantages of Overmolding
(1)Reduced expenses
Adopting overmolding is a deliberate step in the realm of cost efficiency, not only in innovation. Plastic overmolding streamlines production, lowers assembly costs, and ultimately lessens the financial footprint of manufacturing by combining several functions into one component.
(2)Flexible
Plastic overmolding is fundamentally flexible. It is not only appropriate for massive production; it also fits nicely in the prototyping and small-volume manufacturing realm. This agility lets companies rapidly iterate, improve designs, and bring goods to market with an efficiency seldom seen in conventional manufacturing processes.
(3)Quick turnaround production
Modern industries require flexibility, a characteristic of plastic overmolding. Overmolding becomes the runner in the production race with rapid tooling ability and shorter lead times. It involves producing components rapidly without lowering quality, not only in quantity.
(4)Minimize vibration and shock.
Beyond looks, plastic overmolding shields against the shock and vibration constant forces. Overmolding serves as a cushion, absorbing shock and lowering vibration to guarantee the component's longevity whether it is a handheld device in regular use or industrial equipment exposed to the rigors of manufacturing.
(5)Extend item life
Durability is a goal as well as a aim. Overmolding has inherent this feature. Its protective coating guards against passage of time, wear, and tear. In a society that values durability, items are not just functional but also resilient—that is, they can survive the passage of time.
The tactile symphony of overmolding is perhaps most harmonious in terms of grip and feel. Whether it is a tool in the hand or a device at the fingertips, overmolding shapes the interaction between a product and its user. It is more than a layer; it is a layer. It is a feeling of comfort and control.
4.Applications of Overmodling
Overmolding is sometimes employed in the automotive sector to create components with several materials and uses. Overmolding, for instance, is used to make door handles, dashboard parts, and steering wheel grips.
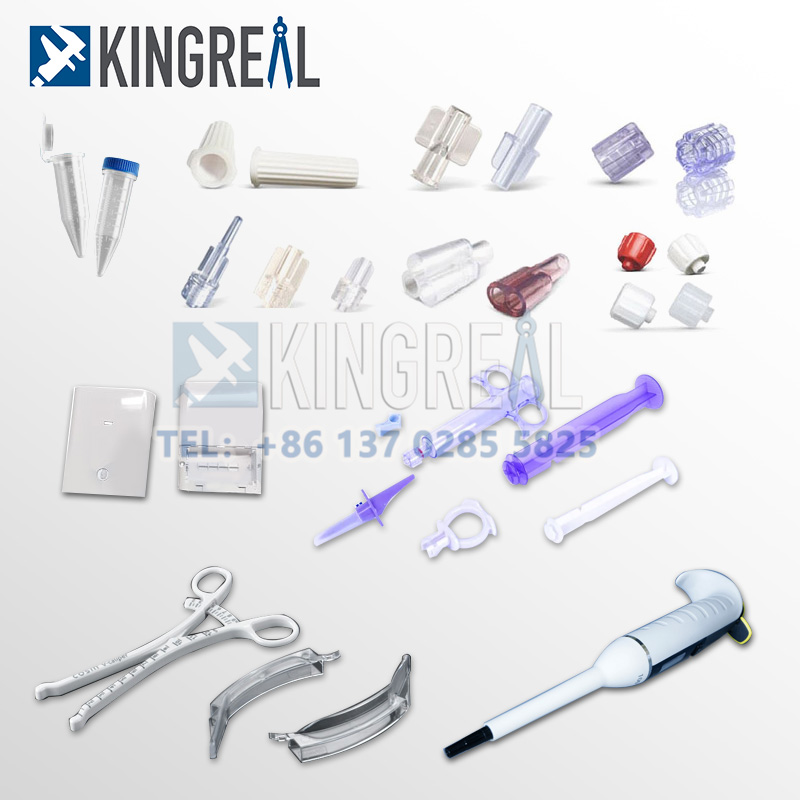
In the production of components with improved durability, flexibility, and grip, overmolding is employed in the medical field. Syringes, catheters, and tubing are among medical devices made from it many times.
Consumer Products: Overmolding is used in the manufacturing of consumer products to enhance aesthetics, utility, and durability. It is frequently employed to make parts for electronics, appliances, and sports equipment.
Industry uses overmolding to create parts with enhanced performance and longevity. It is sometimes used to make seals, bearings, and gears among other components for machinery and equipment.The aerospace sector uses overmolding to create lightweight, functional components.