Full Solution For Aviation Equipment Injection Molds
—
KRMOLD Aviation Equipment Injection Molds are designed to help customers in the aerospace manufacturing industry produce injection molding tools for composite materials. Injection molds play a key role in the manufacture of composite parts by producing parts that meet the extreme conditions of high temperature and pressure and the stringent dimensional requirements of aerospace manufacturing.
Commonly injection molded aerospace components include aircraft wings, fuselage panels, turbine housings, turbine blades, etc. Prior to completing the injection molding process, KRMOLD designers and customer engineers need to communicate with each other about the detailed requirements of the component to ensure that the part meets the performance criteria. Molded parts used in the aerospace manufacturing industry must be manufactured to the highest level of perfect specifications and exacting dimensional manufacturing accuracy, and through this attention to detail, injection molded parts products will be able to withstand the demanding conditions required for aerospace applications.
Aerospace injection molds help to form various types of molten malleable plastics into desired shapes. In this process, polymer particles are melted and injected into the mold, and the molten plastic can be formed into virtually any shape. In order to meet the production needs and development of the aerospace manufacturing industry, KRMOLD pays more attention to the structural design of molds and the field of high-precision injection molding, through the selection of raw materials for the molds and the design of complex runners to achieve a variety of aerospace manufacturing needs for the production of precision and large parts.
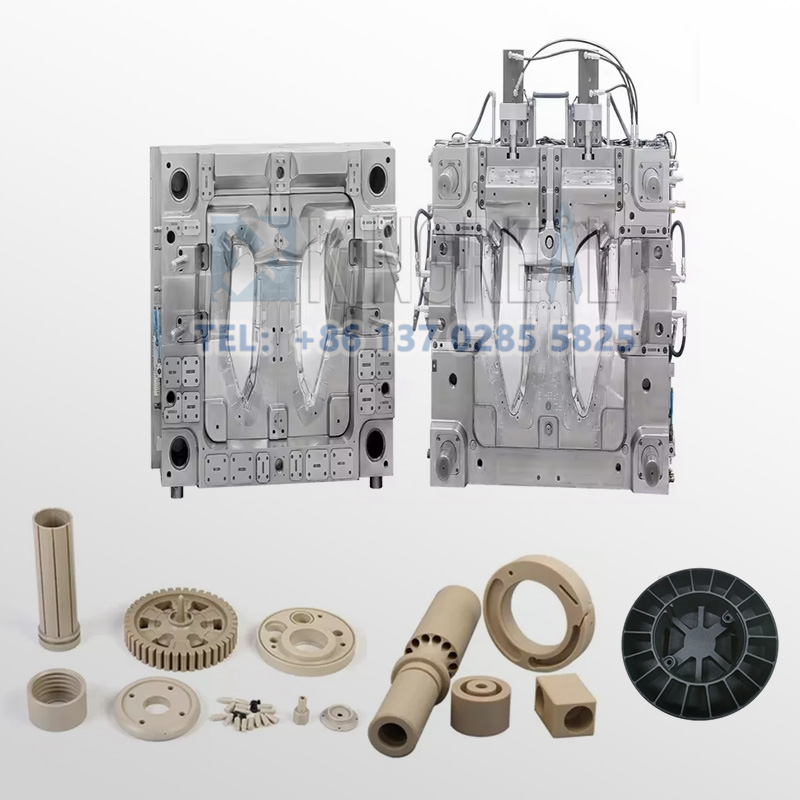
Aerospace Plastic Injection Mold Services
—
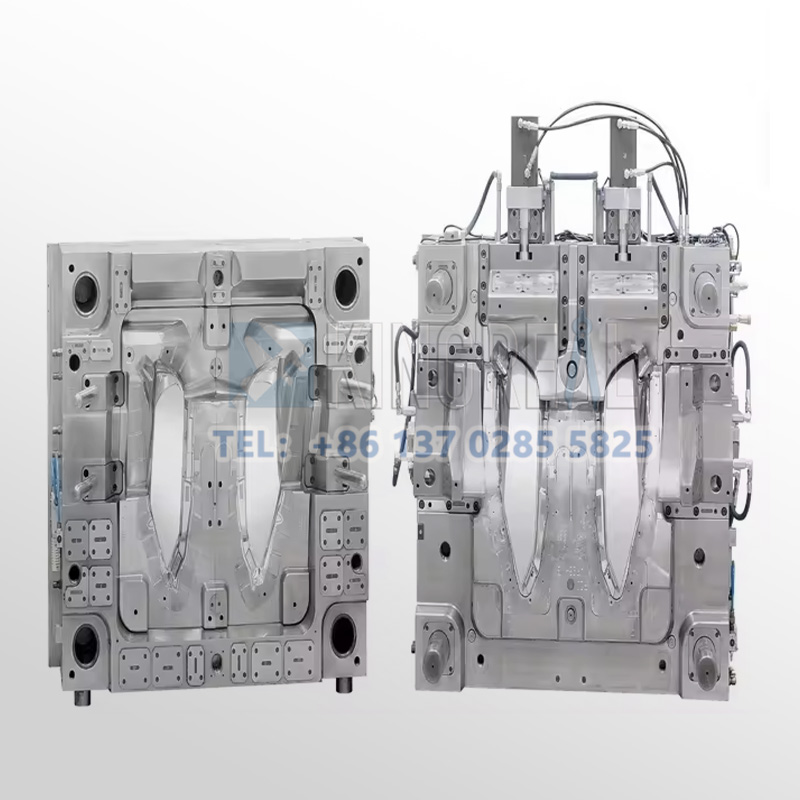

Before the production of injection molds, KRMOLD has a professional design team to communicate the demand and design for the products that customers need to produce. We analyze the material properties, tolerance and size requirements and production batch size of the aerospace parts, etc. We design the injection mold model to optimize the structure of the injection mold through 3D modeling of the parts and products.
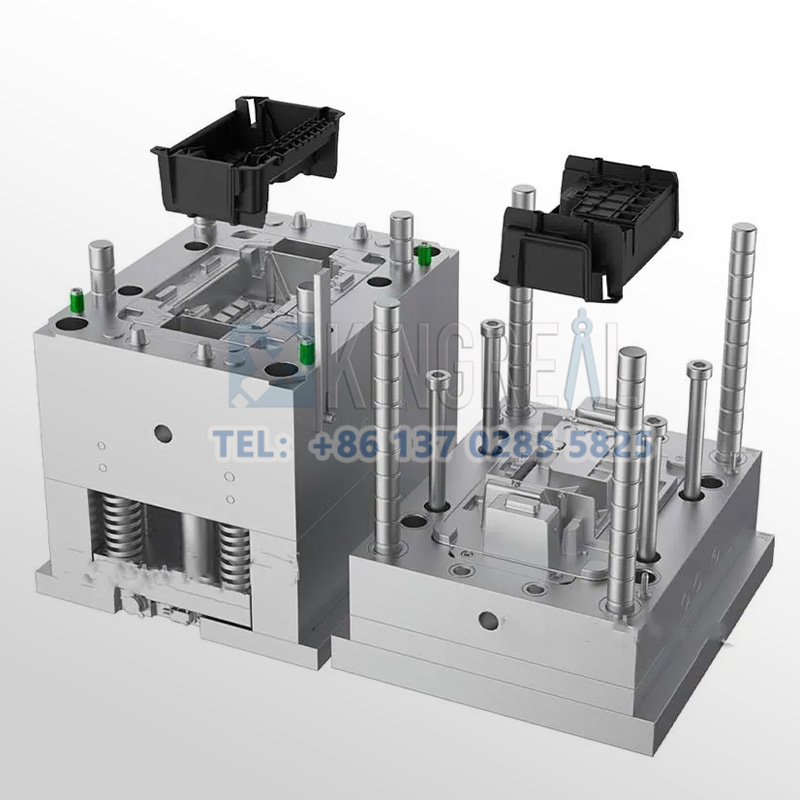
After the completion of the requirements and design, KRMOLD will start the formal injection mold production process, using common mold steel for the basic surface treatment process, followed by CNC precision machining, CNC milling to remove most of the material, the formation of the initial profile, and then by EDM for the complex surfaces of the mold and deep-cavity structure of the processing. After the production of the preliminary structure of the mold is completed, mirror polishing and mold fit are carried out.
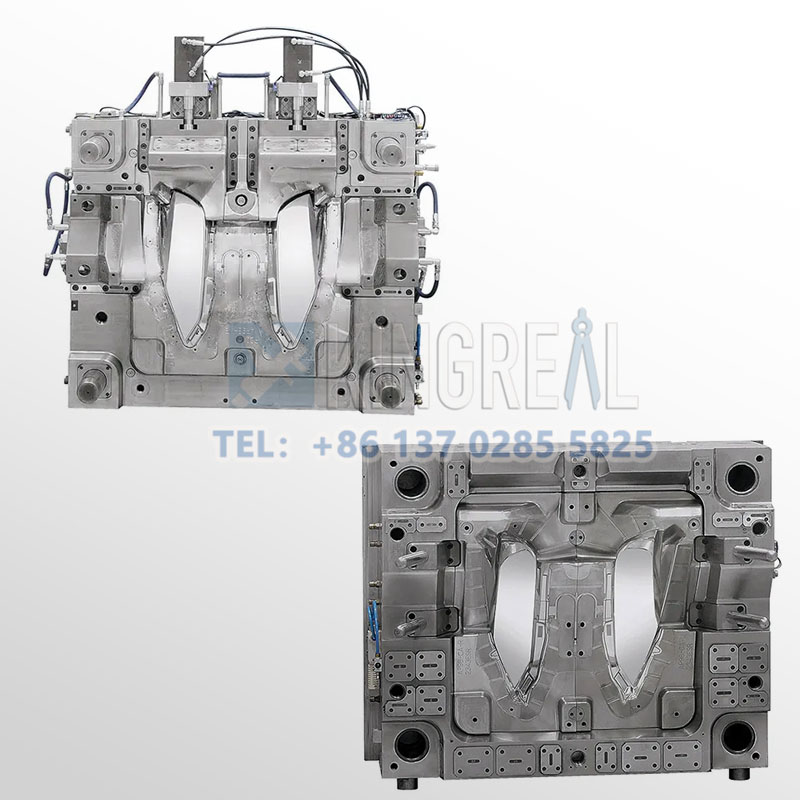
After the production of aerospace plastic injection molds, the precision of the equipment is inspected using precision inspection equipment such as quadratic and cubic yuan. Meanwhile, KRMOLD will arrange the assembly and trial molding process of the injection molds in the factory, install the molds on the injection molding machine, set the appropriate process parameters, and carry out the trial production of small batch to check whether the products have any quality problems such as shrinkage, bubbles, war-page, short shot, and burrs.
Common Aerospace Injection Mold Molding Processes
——
1.Gas-Assisted Injection Molding, GAIM
Aerospace injection molds use the GAIM injection molding process, after the molten plastic is injected into the mold, high-pressure nitrogen is injected into the cavity to push the plastic to flow, so that a hollow structure is formed inside the part.GAIM injection molding is usually used for parts with uneven wall thicknesses, and it can reduce internal stresses and avoid warping. It can reduce internal stress, avoid warping, and produce lightweight and high rigidity aerospace parts.
Representatives of injection molds: such as seat armrests, instrument panel frame injection molds.
Aerospace injection molds use Two-Shot Injection Molding to inject two different plastic materials sequentially in the same mold to form a multi-material or two-color effect, which is commonly used to produce multi-material combination of aerospace interiors, control panels, buttons and other injection molded products.
3.Conventional Injection Molding
Conventional Injection Molding is the most common injection molding process, the production process is usually to heat the plastic particles so that it melts to the flow state, high-pressure injection mold cavity, fill the mold cavity. It is then cooled and cured, and the part is shaped and demolded. It is commonly used to produce small to medium sized parts such as interior parts for aerospace equipment, electronic connectors, pipe fittings, and other small and medium sized parts.
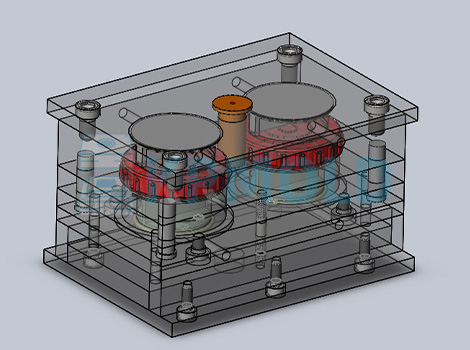


Common Injection Molding Materials for Aerospace Parts
——
“In the aviation industry, plastic parts need to meet the requirements of lightweight, high strength, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, flame retardant and so on. Therefore, the materials commonly used in aerospace injection molding are mainly high-performance engineering plastics, and KRMOLD aerospace industry injection molds can meet the production needs of different materials.”

1. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK)
Aerospace parts molded by injection molding using polyether ether ketone as a raw material have the advantages of high temperature resistance, high strength, and corrosion resistance, and can be used for a long time in the vicinity of an aircraft engine, and are resistant to fuel oils, hydraulic fluids, solvents, etc. Common injection molded parts include aviation pipes, body interiors, electronic connectors, and bearings. Common injection molded parts include aviation tubes, fuselage interiors, electronic connectors and bearings, etc.
2. Polyetherimide (PEI, Ultem®)
Aerospace parts molded by injection molding using PEI as a raw material can achieve high rigidity, impact resistance, and excellent electrical insulation properties, ensuring that the parts will not be deformed by long term use, and are suitable for use in high-stress environments. Common injection molded parts include aviation seat parts, cabin window frames, cable supports and radomes.
3. Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS)
Generally speaking, PPS is used in the injection molding of aerospace industry parts such as fuel pipes, engine parts, electrical connectors, gears and heat shields, etc. It is capable of high temperature resistance, high dimensional stability and good abrasion resistance, and is suitable for friction parts.
FAQ:
1.How to get a quote for custom injection molds?
Specify the type of plastic (e.g. PP, ABS) and post-processing requirements (e.g. spraying, silk-screen printing), and provide 2D or 3D plastic part drawings should be provided. At the same time, provide the production volume, appearance requirements, tolerance standards, etc.
2. How long does it take to get a quote for an injection mold?
Generally speaking, our engineers will start to prepare the quotation immediately after the customer provides the complete production requirements. Usually it takes about 1-3 days.
3. What is the lead time for injection molds?
The lead time for regular injection molds is usually 30-60 days, and may be longer for complex molds. For example, the typical lead time for liquid silicone molds is around 60 days, covering design, manufacturing, mold testing, etc.
Specify the type of plastic (e.g. PP, ABS) and post-processing requirements (e.g. spraying, silk-screen printing), and provide 2D or 3D plastic part drawings should be provided. At the same time, provide the production volume, appearance requirements, tolerance standards, etc.
Generally speaking, our engineers will start to prepare the quotation immediately after the customer provides the complete production requirements. Usually it takes about 1-3 days.
The lead time for regular injection molds is usually 30-60 days, and may be longer for complex molds. For example, the typical lead time for liquid silicone molds is around 60 days, covering design, manufacturing, mold testing, etc.
High-precision processing technology: High-precision equipment such as CNC machining centers (CNC) and electric discharge machining (EDM) are used to optimize the design process in combination with CAD/CAM software. Quality control: Inspection of key dimensions of the mold by Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) and verification of multiple sample batches during the trial molding stage. Material Selection: Use die steel with high wear resistance (e.g. H13, S136) and surface treatment (e.g. nitriding, chrome plating) for die nuts to extend the life.
After every 50,000 molds, check the guide pillar, ejector pin and other wear parts, and clean up the residual plastic and rust on the mold surface. Use high temperature grease for sliding parts (e.g. tilt top, slider) to reduce friction loss. Ensure that the water circuit is smooth and the temperature difference is ≤5℃ to avoid cracking of the mold due to thermal stress.
Mould cost of materials accounted for about 30-40% (such as 1 ton of P20 steel price of about 20,000 yuan), processing costs accounted for more than 50% (CNC labor hourly rate of about 80-150 yuan / hour). Small batch production can choose aluminum mold or simplify the structural design; more than 100,000 pieces is recommended to use carbide inserts to enhance life!
Mould injection products need to fully meet the design requirements (such as size, appearance), and can be continuous and stable production. Mold marking, inspection reports (such as material hardness test) and engineering drawings should be complete.
Mould steel (such as S136H, NAK80 and other imported materials cost more) and the type of mold embryo (aluminum mold short-term cost is low but short life) directly affect the cost, the use of CAD/CAE/CAM design technology, hot runner system, etc. will increase the upfront investment, but can enhance the long-term benefits (such as reducing the sprues, increase production capacity).