KINGREAL UNIVERSAL IND., LTD
Phone
+86-13702855825| 1 | Advantages of Medical Injection Molding |
| 2 | Applications of Medical Injection Molding |
| 3 | Materials Used in Medical Injectable Components |
| 4 | Considerations When Selecting Medical Injection Molding Materials |
| 5 | Common Types of Plastic Injection Molding |
Medical device housing injection molding produces durable and reliable medical-grade components that meet FDA standards. Currently, medical injection molding is the preferred process for manufacturing the most advanced medical devices, with leading laboratory facilities and medical equipment manufactured using medical device housing injection molding.
Medical injection molding is cost-effective and offers excellent accuracy and consistency. This is crucial when large production runs are required. This article will serve as a beginner's guide to the medical device housing injection molding process.

1.Advantages of Medical Injection Molding
01. Wide range of material options for medical injection molding
Plastic injection molding offers the widest range of material options. While medical injection molding narrows the range of materials available, many materials are still suitable for manufacturing medical-grade parts. KRMOLD will discuss this more later in this guide.
02. Cost-effectiveness for medical device housing injection molding
The way the medical device housing injection molding process is set up helps reduce unnecessary injection molding costs—large-scale production delivery and high-volume manufacturing help maximize process efficiency. Therefore, when producing large quantities of medical injection parts, the medical injection molding process can reduce the cost per part.
03. Durability for medical device housing injection molding
One well-known fact about the plastics used in medical injection molding is their durability. These materials offer unwavering strength and resistance to adverse environments and use. Therefore, products produced using this process can comfortably withstand heat, blunt force, and vibration without cracking or breaking. Furthermore, they remain unaffected by the high temperatures experienced during sterilization in autoclaves.
04. Exceptional accuracy for medical injection molding
Exceptional precision is essential in the medical device housing injection molding process for the medical device industry. Due to the tight tolerances, every inch, millimeter, or centimeter matters. Furthermore, skilled injection molding equipment must be used to achieve this high level of precision.
05. Resistance to contaminants for medical injection molding
The materials used in this production process readily resist the ingress of contaminants. Furthermore, they require minimal sterilization to maintain sterility. This factor makes it easy for the materials to meet FDA standards and other regulations.
2.Applications of Medical Injection Molding
The applications of medical device housing injection molding are diverse. Medical suppliers employ this process because it easily allows their products to meet required quality and safety standards. Medical injection molding is also used in the following areas:
-Dental X-ray equipment
-Orthopedics
-Components and devices for drug delivery
-Laboratory supplies, such as test tubes, beakers, and other containers
-Surgical instruments and equipment for surgical instrument preparation
-Casings, housings, and casings for medical and laboratory equipment
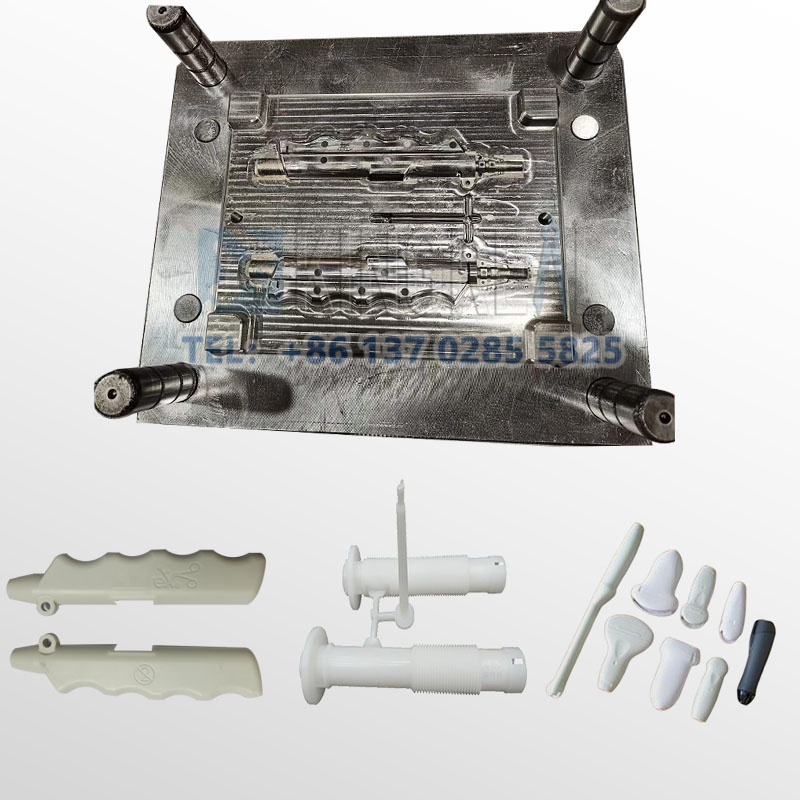


3. Materials Used in Medical Injectable Components
The medical device housing injection molding process uses a wide range of material options to manufacture medical and pharmaceutical components. A variety of medical device housing injection molding materials are used, making the process highly efficient. Some of these include:
-Polypropylene (PP): Due to its strength and durability, it is one of the most commonly used plastics in the industry. Polypropylene contains strong chemical bonds, making it a preferred material for manufacturing medical devices, such as beakers and test tubes.
-Polyethylene (PE): This material is a staple in the thermoplastics industry. It is used in many industrial and commercial machinery components with varying stiffness levels. It comes in many different durability grades, some of which are LDPE, HDPE, and UHMV. UHMV is a component of most hip, leg, and other joint prostheses.
-Polystyrene (PS): This is a strong plastic with little elasticity. It is inflexible and exhibits high levels of impact resistance and processability. It is primarily used for easily customizable surfaces with good dimensional stability and aesthetics.
-Polyetheretherketone (PEEK): This is a thermoplastic known for its high performance and excellent mechanical properties. It offers high levels of resistance to abrasion, radiation, tracking, and thermal degradation.
-Silicone: This is the material of choice when flexibility is a primary requirement for medical device components. Its ability to impart extreme durability and biocompatibility to parts is second to none in the industry. It is also affordable and reduces costs in high-volume production.
4.Considerations When Selecting Medical Injection Molding Materials
The medical device housing injection molding process for medical devices is highly critical, with a high probability of failure. Therefore, several factors need to be considered before and during the design, planning, and operation of the procedure. These include:
01. FDA requirements for medical device housing injection molding
For medical component manufacturing, FDA requirements are the target standard for all processes. Sterility and cleanliness regulations are stringent and must be strictly adhered to. At all stages of production, ensure that all inputs meet or exceed specified standards. To achieve medical-grade certification, the factory must pass standards for both components and the production process.
02. Withstand the sterilization process for medical injection molding
This is a minimal but critical requirement for medical products. All enclosures, equipment, or components that come into contact with the human body must be contamination-resistant. They should also survive the sterilization process without damage.
03. Operating environment for medical device housing injection molding
The ability to withstand adverse conditions is a key consideration for medical device housing injection molding materials. They must be reliable and durable when subjected to heat, corrosion, liquids, vibration, and other human motion. Most plastics used in this process rank high in this requirement.
04. Durability and strength for medical injection molding
Fragile plastics should be avoided in manufacturing equipment to avoid or minimize biohazards in the medical field. Therefore, each selected material should demonstrate satisfactory durability before use. More importantly, it should be able to demonstrate high levels of tensile strength.
05. General use for medical injection molding
Always consider the material's intended use before selecting. For example, disposable materials such as syringes, needles, tubing, and connectors should be transparent, flexible, and easily sterilized. Similarly, surgical injection parts should be lightweight and ergonomic.


5. Common Types of Plastic Injection Molding
Manufacturers offering injection molding services use a variety of plastic molding technologies to produce medical-grade parts. However, here, KRMOLD will examine four common types, including:Thin-Wall Injection Molding, Gas-Assisted Injection Molding, Metal Injection Molding, Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding.
01. Thin-Wall Injection Molding
Thin-wall injection molding is one of the most common processes in medical device housing injection molding. It is used to produce tools or effects that enhance functionality and patient comfort. The walls of injected parts for medical devices are significantly thinner than those of the complete component, typically less than 1 mm.
Device manufactured in this manner place high demands on their materials. Despite the thin walls, the device or tool maintains a certain degree of integrity and durability. Due to these requirements, the base material is often plastic (particularly LCP or polypropylene, or even nylon).
The material used in production depends largely on the object being manufactured. These molds (prototypes) undergo extensive testing to ensure their usability.
Devices produced using this type of medical device housing injection molding include wearables, surgical tools, and catheter ablation devices.
02. Gas-Assisted Injection Molding
This is a more complex type of molding. With conventional molding, thicker parts tend to dry or cure more slowly than thinner-walled parts. This is because there isn't enough pressure to properly pack the resin and distribute it evenly.
As a result, the resin ends up looking misshapen, unsightly, and structurally weaker than it should be due to sink marks. Gas-assisted injection molding is a solution to this problem in plastic injection-molded medical parts.
The process involves passing gas through channels built into the mold. The gas (nitrogen) is passed through the middle of these thicker sections. This creates the pressure needed to press the resin tightly against the mold, resulting in smooth, structurally sound parts with zero sink marks.
Gas-assisted injection molding is not suitable for tool designs with sharp corners, as the gas pressure decreases if the flow doesn't follow a straight line. However, this type of molding is more suitable for producing complex parts.
03. Metal Injection Molding
The use of metal in medical device manufacturing is a technology we cannot ignore. This is because metal devices play a crucial role in devices requiring high density, small size, and maneuverability. This doesn't detract from the numerous uses and advantages of traditional 3D printing, medical injection molding, or gas-assisted molding.
Typically, atomization technology creates a powder mixture from the desired metal. This powder is formed into pellets (stock material) and contains a binder to make it easier to mold.
After injection, the binder is removed through various methods, including solvents, catalytic processes, hot furnaces, or even a combination of these. This leaves a molded part with 100% density.
04. Liquid Silicone Rubber Injection Molding
Some medical devices, such as tubing and respiratory masks, are difficult to maintain hygienically. Therefore, liquid silicone rubber injection molding is often best suited for producing such devices.
The stringent requirements of this process require a hygienic production environment. This environment ensures that no ambient air, dust, or moisture can settle on the mold or mixture as it solidifies. The rubber-like substance produced by this process is highly chemically resistant.
Silicone does not react with biological tissue, making it more suitable for safe implantation. However, this liquid silicone rubber injection molding process requires several steps. This also depends on the desired properties of the resulting silicone product.