
KINGREAL UNIVERSAL IND., LTD
Phone
+86-13702855825Automotive instrument panel molds allow for the mass manufacture of top-notch car instrument panels satisfying industry criteria for lifespan, looks, and performance. Car instrument panels incorporate a range of control mechanisms, displays, and safety systems as they are absolutely necessary component of automotive production. As manufacturing techniques improve and consumer expectations grow, KRMOLD can design and create even higher-quality car instrument panel molds for complex structures and fine detailing. This article from KRMOLD will explore the manufacturing process, key design considerations, and advantages of high-precision car instrument panel molds.
What are Automotive Instrument Panel Molds?
| Shaping the instrument panel—a key feature of the interior of the automobile—car instrument panel molds are essential. Key features like the speedometer, infotainment system, air vents, and control buttons are shaped by these automobile instrument panel forms. The automotive instrument panel molds have to guarantee exact measurements, particular textures, and exacting details for every panel. The automotive instrument panel molds have to have a great surface finish because the instrument panel is a rather visibly prominent element in an automobile. | 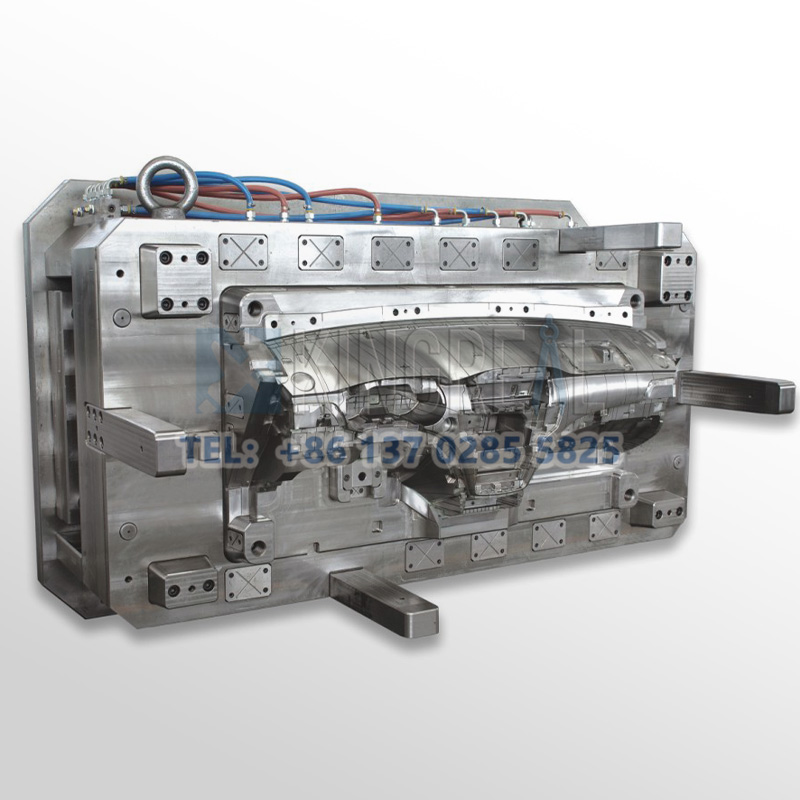 |
What Materials are Used in Car Instrument Panel Molds?
The materials used in automotive instrument panel molds must possess high strength, heat resistance, and durability. High-quality injection molding processes for car instrument panels ensure smooth production and reduce defects. High-grade steel is the most commonly used material for manufacturing automotive instrument panel molds due to its excellent strength, heat resistance, and durability; grades such as P20, H13, and S136 are widely used. Aluminum is another commonly used material; although its strength is not as high as steel, its light weight and ease of processing make it suitable for small-batch production. Nickel alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for manufacturing long-lasting molds.
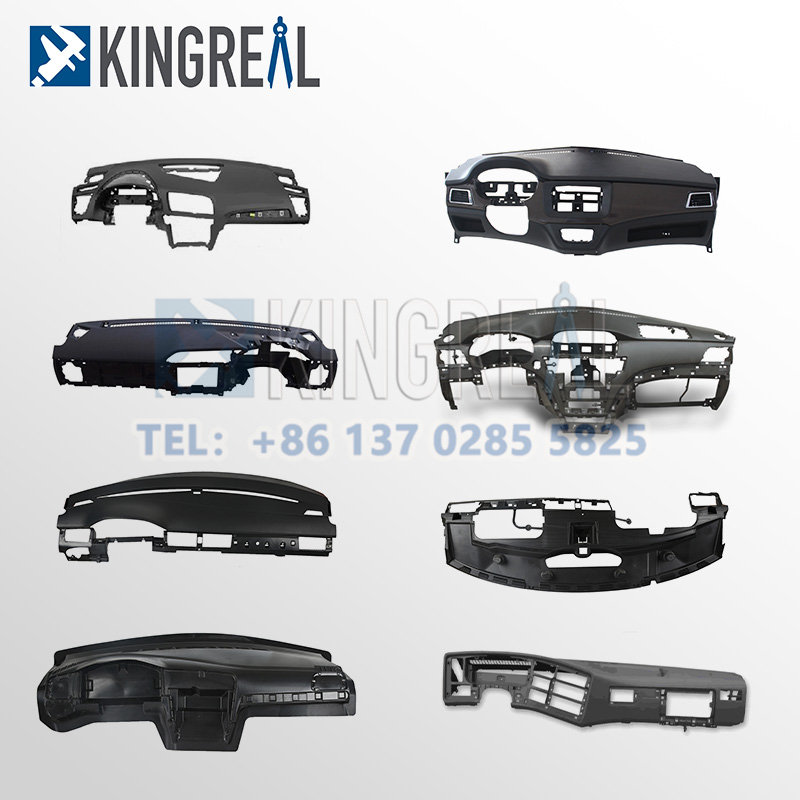
Automotive interior plastic components are typically made of thermoplastics. Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS) is a common material due to its excellent impact resistance and surface quality. Polycarbonate/ABS blends (PC/ABS) offer high heat resistance and toughness. Polypropylene (PP) is widely used due to its light weight and cost-effectiveness, while glass fiber reinforced plastics are used in high-strength applications where durability is a critical requirement.
Key Elements of Car Instrument Panel Mold Structure Design
1. Parting line design of car instrument panel mold:
The main parting line is determined based on the product's maximum projected profile and ejection requirements.
1.1 Solving complex undercuts: A precision sliding core (slider), driven by a bevel pin, hydraulic system, or motor, ensures accurate and reliable movement.
1.2 Solving internal undercut issues: A lifter (internal slider) is used for lateral core pulling during ejection. This compact design places high demands on the ejection system layout.
2. Gating system design of car instrument panel mold:
2.1 Gate type selection: Due to the large size and complex structure of the instrument panel, a multi-point valve gate hot runner system is often used to achieve balanced filling, reduce weld lines, improve material utilization, and shorten the molding cycle.
2.2 Runner balancing: Ensures that the molten plastic flows uniformly and simultaneously to the end of the cavity, preventing local overfilling or underfilling.
2.3 Cold slug well design: Effectively captures and isolates the leading cold slug, preventing surface defects or gate blockage.
3. Temperature control system design of car instrument panel mold:
3.1 Dense cooling circuit: Multiple cooling channels are placed close to the cavity, core, and slider surfaces to achieve efficient and uniform heat exchange.
3.2 Zoned temperature control: Differentiated temperature management is implemented for transparent areas, thick cross-sections, and high-gloss surfaces to optimize cooling efficiency and minimize internal stress.
3.3 Media selection: Standard cooling water, chilled water, or oil-cooled units are used depending on the required temperature control accuracy.
4. Ejection system design of car instrument panel mold:
4.1 Multi-point balanced layout: The ejector pin, ejector sleeve, and stripper plate are combined to ensure deformation-free ejection of large, thin-walled parts.
4.2 Ejection path planning: Critical features (e.g., clamps, ribs) are avoided to prevent ejection marks or damage.
4.3 Return and early return mechanism: The ejection system is ensured to fully and accurately reset before automotive instrument panel mold closure to prevent interference with the slide block.
5. Ventilation system design of car instrument panel mold:
5.1 Sufficient exhaust channels: Exhaust channels or inserts are positioned at the melt flow ends, parting lines, insert connections, and around ejector pins.
5.2 Depth Control: Ventilation channel depth is typically maintained within 0.015-0.03 mm to prevent burrs.
6. Mold base and guiding system of car instrument panel mold:
6.1 High-rigidity mold base: Provides sufficient support strength and resistance to deformation.
6.2 Precision guiding: High-precision guide pillars and guide sleeves are used to ensure precise and deviation-free movement of the automotive instrument panel mold half and slide.
What are the Advantages of Using High-precision Automotive Instrument Panel Molds?
-Accurate geometric replication: Faithfully reproduces designed surfaces, including complex ribs, clips, positioning pillars, wiring channels, vent structures, and decorative textures.
-Optical component molding: Produces transparent or translucent plastic parts with high light transmittance and stress-free surfaces for pointer windows, warning light areas, display covers, etc.
-Multi-material integration capability: Supports two-color/multi-color injection molding of rigid substrates (such as PVC, TPU) with soft-touch surfaces, or provides precision substrates for subsequent overmolding processes.
-Dimensional stability guarantee: Maintains micron-level tolerances under the high temperature and pressure of injection molding and environmental changes during subsequent use.
-High-efficiency production and long lifespan: Achieve rapid cycle times and withstand millions of injection cycles while maintaining critical dimensions and surface quality.
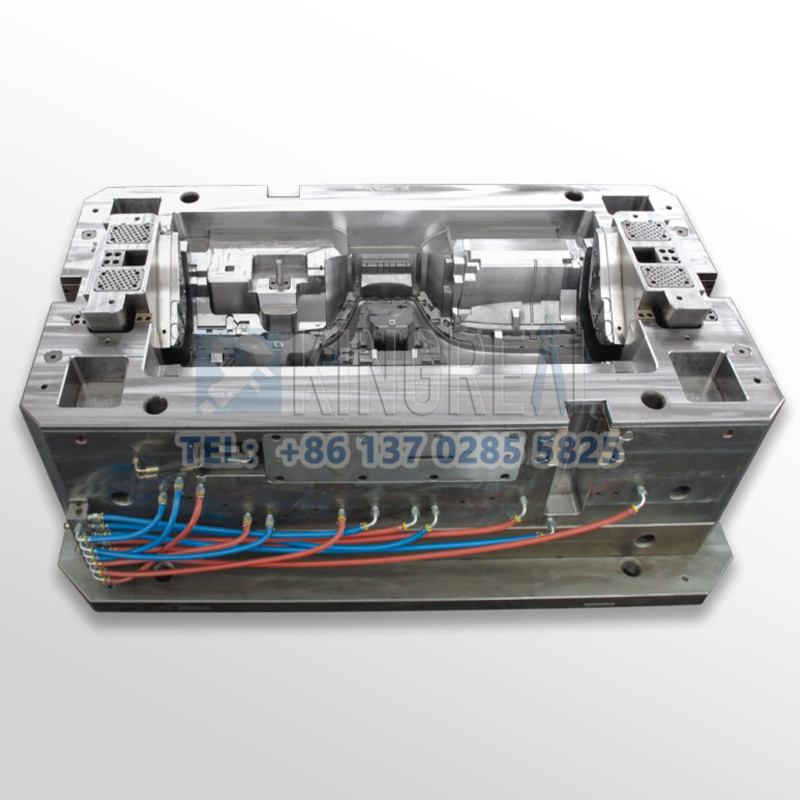

Automotive Instrument Panel Mold Manufacturing Process
Automotive instrument panel mold manufacturing translates design intent into physical form through a series of precision machining and processing steps:
1. Rough machining and pre-treatment for automotive instrument panel mold:
1.1 Mold base blank preparation: Procure blanks according to design specifications.
1.2 Datum surface machining: Establish precise machining datums.
1.3 Preliminary cavity/core contour machining: Remove large blocks of material.
1.4 Pre-drill structural holes, water pipes, etc.
2. Heat treatment for automotive instrument panel mold:
Heat treat critical components to achieve the required combination of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance.
3. Precision machining for automotive instrument panel mold:
3.1 CNC high-speed milling: Machining complex free-form surfaces, ribs, and fine features.
3.2 EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Machining deep grooves, narrow gaps, sharp corners, and hardened areas (e.g., fine textures) that milling cannot reach.
3.3 Wire EDM: Machining precision through holes and insert contours.
3.4 Deep hole drilling: Creating long-distance cooling channels.
3.5 Grinding: Ensure dimensional accuracy and surface finish of critical mating surfaces (parting line, slider interface), guide pillars, and bushings.
4. Surface treatment and special processes for automotive instrument panel mold:
4.1 Texture etching: Utilize photochemical etching technology to create leather textures, wood grain patterns, geometric patterns, etc., on the cavity surface.
4.2 Polishing: Achieve a mirror finish (Ra≤0.01μm) in transparent and high-gloss cavity areas.
4.3 Surface hardening: Apply PVD, CVD, TD coatings, or nitriding to enhance the wear resistance and corrosion resistance of critical areas.
4.4 Component precision inspection: Rigorously inspect the dimensions, geometric tolerances, and surface quality of all machined features using CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine), profilometers, and surface roughness testers.
5. Car instrument panel mold assembly and testing: Thoroughly clean all components.
5.1 Perform precision assembly according to drawings, ensuring smooth movement of all dynamic components within specified clearances.
5.2 Automotive instrument panel mold closure test: Verify parting line contact.
5.3 Injection molding machine trial molding: Verify filling, dimensions, appearance, and ejection. Make necessary automotive instrument panel mold modifications.
Looking for Advanced Automotive Instrument Panel Molds?
KRMOLD specializes in designing, developing, and manufacturing high-quality, customized automotive instrument panel molds, providing innovative solutions to the automotive industry. Whether it's a luxury car or an economy car, regardless of brand or size, KRMOLD premium automotive instrument panel molds ensure that every vehicle's interior meets modern safety and design standards.