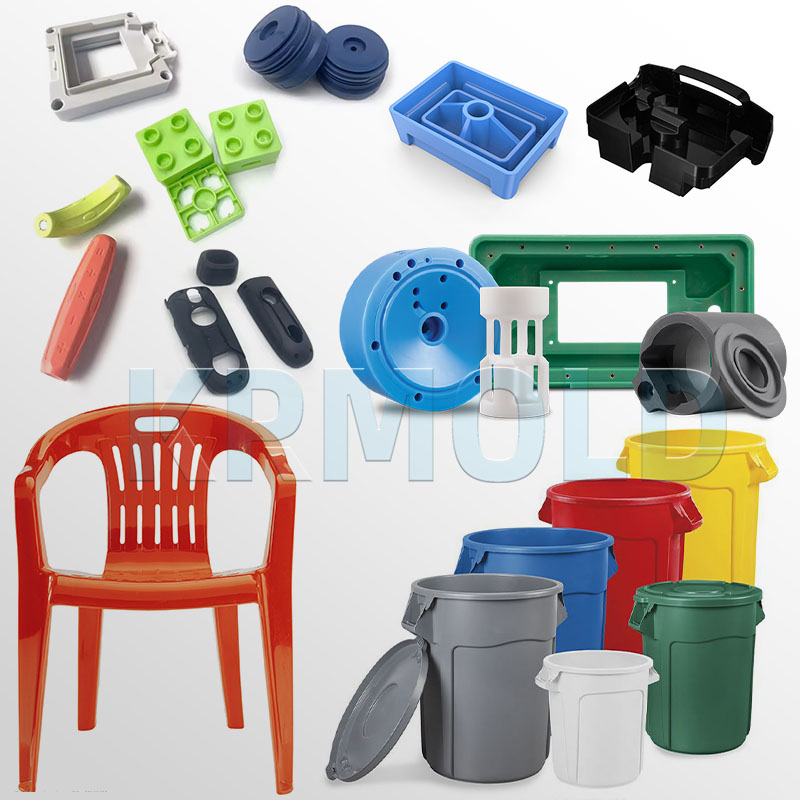
KINGREAL UNIVERSAL IND., LTD
Phone
+86-13702855825| 1 | Drying of ABS Plastic |
| 2 | Injection Temperature |
| 3 | Injection Pressure |
| 4 | Injection Speed |
| 5 | Mold Temperature |
| 6 | Material Volume Control |
| 7 | Injection Molding Machine Selection |
| 8 | ABS Injection Molding Precautions |
| 9 | Applications of ABS Plastic Injection Molding |
One well used technique for plastics processing is ABS injection molding. Many sectors choose it as their preferred material because of its great mechanical qualities and simple processing. This post will offer a thorough examination of the ABS plastic injection molding process, including drying, injection temperature, pressure, speed, mold temperature, and several other considerations. To assist you better understand and apply ABS injection molding technology, choose injection molding equipment and manage material quantity.
1. Drying of ABS Plastic
ABS plastic has great hygroscopicity and is very susceptible to water. Before ABS injection molding, then, it has to be absolutely dried and preheated. In addition to helping to remove surface flaws brought on by moisture—such firework-like bubbles and silver streaks—this improves the plasticizing effect and lowers surface color dots and moire. To ensure that the moisture content of ABS raw materials is below 0.13%, drying conditions should be adjusted according to the season and climate:
During dry seasons or winter, drying should be performed at 75-80°C for 2-3 hours.
In humid summer weather, the drying temperature should be increased to 80-90°C and the drying time extended to 4-8 hours. For parts requiring extremely high gloss or complex shapes, the drying time can be increased to 8-16 hours.
To prevent moisture absorption after drying, it is recommended to convert the hopper to a hot air dryer and strengthen humidity monitoring to prevent overheating during unexpected production interruptions. Furthermore, the proportion of recycled material should be kept below 30%, and recycled material should not be used in electroplating-grade ABS.
2. Injection Temperature
During ABS plastic injection molding, controlling injection temperature is absolutely necessary. ABS's melt viscosity is affected by temperature changes. Excessively high temperatures can induce thermal degradation in heat-resistant ABS, hence raising its melt viscosity and impacting abs injection molding quality. The ideal plasticizing temperature range is 220-250°C, and different types of ABS have different suitable melt temperatures:
The furnace temperature of a plunger-type injection molding machine should be maintained between 180-230°C;
The furnace temperature of a screw-type injection molding machine should be controlled between 160-220°C. Remember that temperature changes at the nozzle and barrel tip can have a major effect on component quality. Defects include weld lines, bad gloss, flash, and discoloration can result from even small changes in temperature. Thus, high-quality ABS plastic injection molding depends on precise temperature management.
3. Injection Pressure
Because ABS molten material is so thick, injection usually calls for a higher injection pressure. Although higher pressure enhances component surface quality, smaller, simpler, or thicker items could be more suitable under lower pressure. The part's surface quality and the extent of silver streak imperfections depend on the pressure inside the mold cavity at the moment the gate closes during the injection process.
Too low pressure causes the plastic to shrink considerably, perhaps producing fogging on the component surface.
Mold sticking is readily caused if the pressure is too great as the friction between the mold surface and the plastic increases.
Therefore, good ABS plastic injection molding depends on correct injection pressure settings.



4. Injection Speed
During ABS injection molding, keeping a medium injection rate is essential for best results. Too quick injection speed can cause the plastic to burn or decompose, releasing gases that could cause weld lines, poor gloss, and Plastic redness near the gate. However, when producing thin-walled and complex parts, a sufficient injection speed is still necessary to ensure effective mold filling.
5. Mold Temperature
Because ABS plastic injection molding temperature is comparatively great, careful mold temperature management is just as crucial. Usually, the mold temperature should be kept between 75 and 85 °C . Fixed mold temperature should range from 70 to 80 °C when making components with a bigger projected area; movable mold temperature should ideally range from 50 to 60 °C . Dedicated mold heating is advised for big, complex, or thin-walled components to help to reduce production cycles and keep a steady mold temperature.
A cold water bath, hot water bath, or other mechanical setup strategy can be used following the part's removal to make up for the cooling time inside the mold cavity.
6. Material Volume Control
Each abs plastic injection molding shot usually only reaches 75% of the nominal shot volume. Controlling the shot volume to almost 50% of the nominal shot volume will help to enhance part quality, dimensional stability, and surface gloss.
7. Injection Molding Machine Selection
Choosing the right injection molding machine is crucial for ABS injection molding. Generally, a standard injection molding machine is recommended, with the following parameters:
Screw length-to-diameter ratio of 20:1;
Compression ratio greater than 2;
Injection pressure greater than 150 MPa.
If master-batch is required or if the product appearance is of high importance, a screw with a smaller diameter is recommended. The clamping force should be between 4700 and 6200 t/m², depending on the plastic grade and product requirements.
8. ABS Injection Molding Precautions
When performing ABS plastic injection molding, the following key considerations should be noted:
Drying: Because ABS resin is hygroscopic, with a water absorption rate of approximately 0.3%, the water absorption rate must be reduced to below 0.2% before molding. Using dry resin can produce parts with a highly polished surface.
Melt Viscosity: ABS melt viscosity is sensitive to molding temperature and injection pressure. Proper temperature and pressure settings will facilitate mold filling.
Shrinkage Control: ABS has a low shrinkage rate, typically 0.4% to 0.8%, enabling the production of products with high dimensional accuracy.
Heat Treatment: Molded parts generally do not require heat treatment. However, if surface plating or painting is required, heat treatment at 75-90°C can be performed to eliminate internal stress.
Mold Design: Avoid design gaps and sharp corners to prevent stress concentration. A draft angle of 1.0° is recommended. The gate thickness should exceed 1/3 of the part wall thickness, and gates should not be located on plated surfaces.
9. Applications of ABS Plastic Injection Molding
ABS injection molding is widely used in various industries, including the following:
Automotive: Ideal for lightweight products, it is often used in door handles, instrument panels, and dashboard components.
Commercial Applications: Widely used in household products such as refrigerator liners, vacuum cleaners, and food processors.
Electrical Industry: Used in electronic equipment housings and computer keyboards.
Construction Industry: Suitable for pipes and fittings due to its high impact resistance and excellent chemical stability. Other applications include musical instruments, sports equipment, and medical materials.
ABS injection molding, with its excellent performance and wide range of applications, has become a vital component of the plastics processing industry. By understanding and controlling the above process parameters, you will be able to better utilize ABS plastic injection molding technology and produce high-quality products.

