
KINGREAL UNIVERSAL IND., LTD
Phone
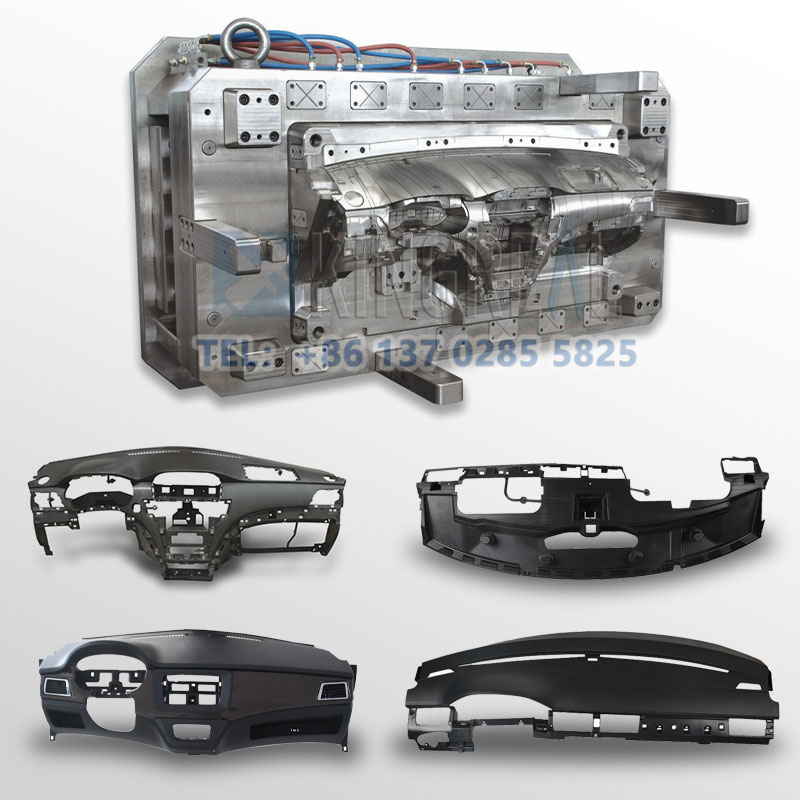
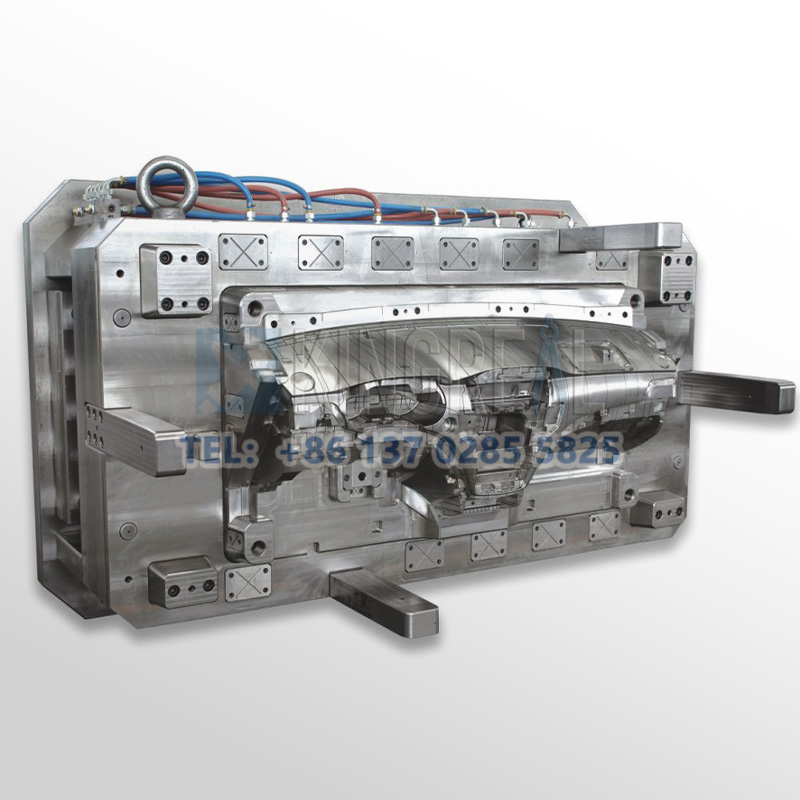
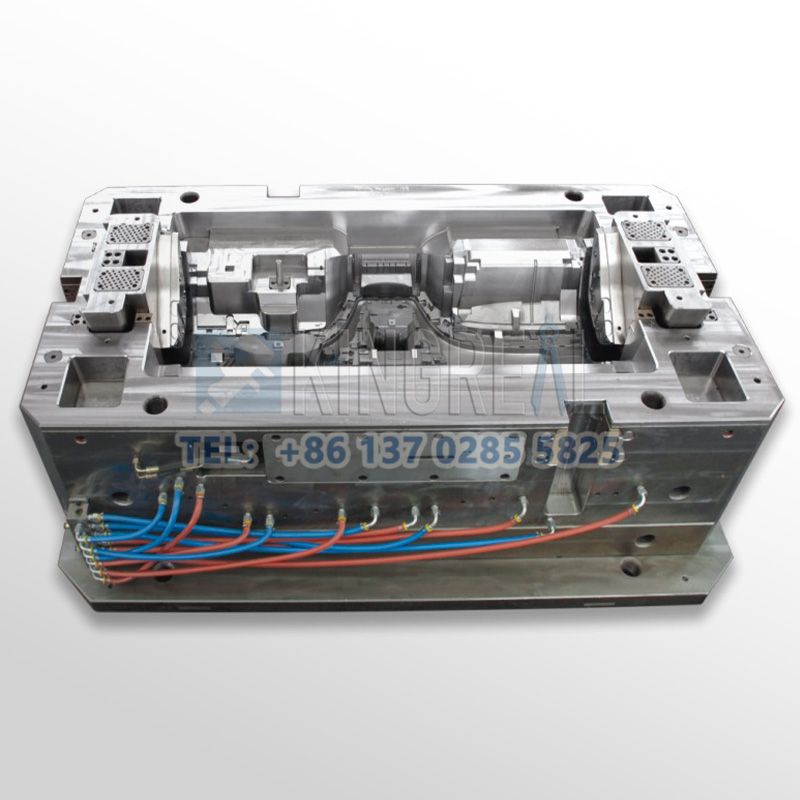
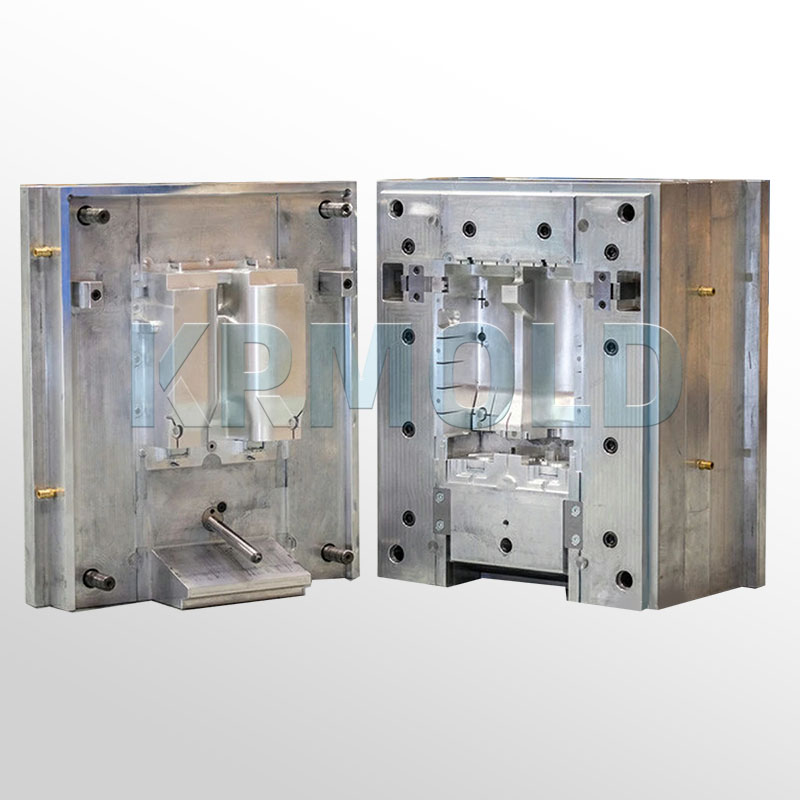
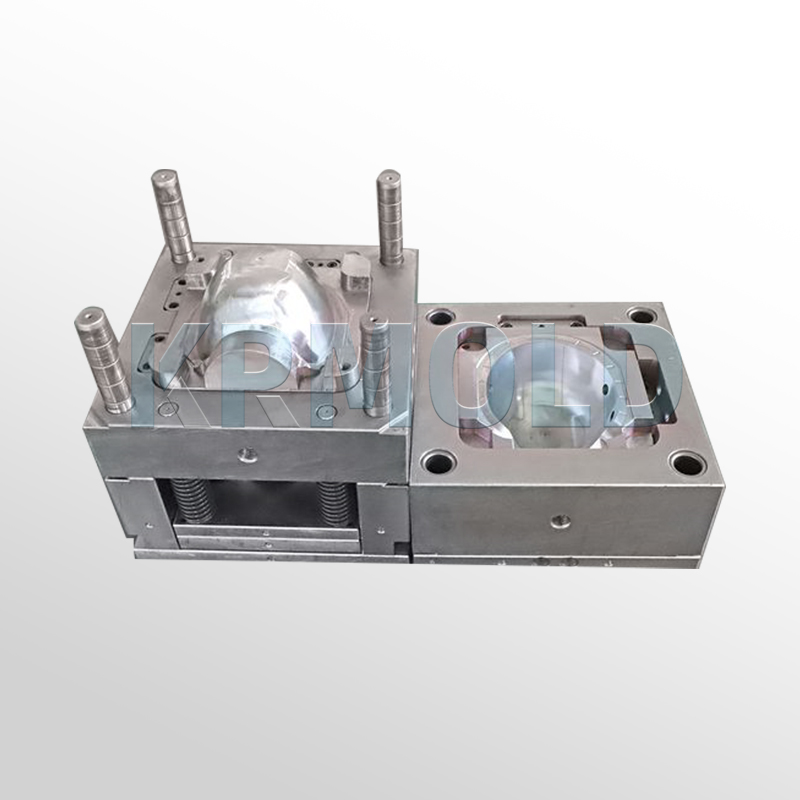
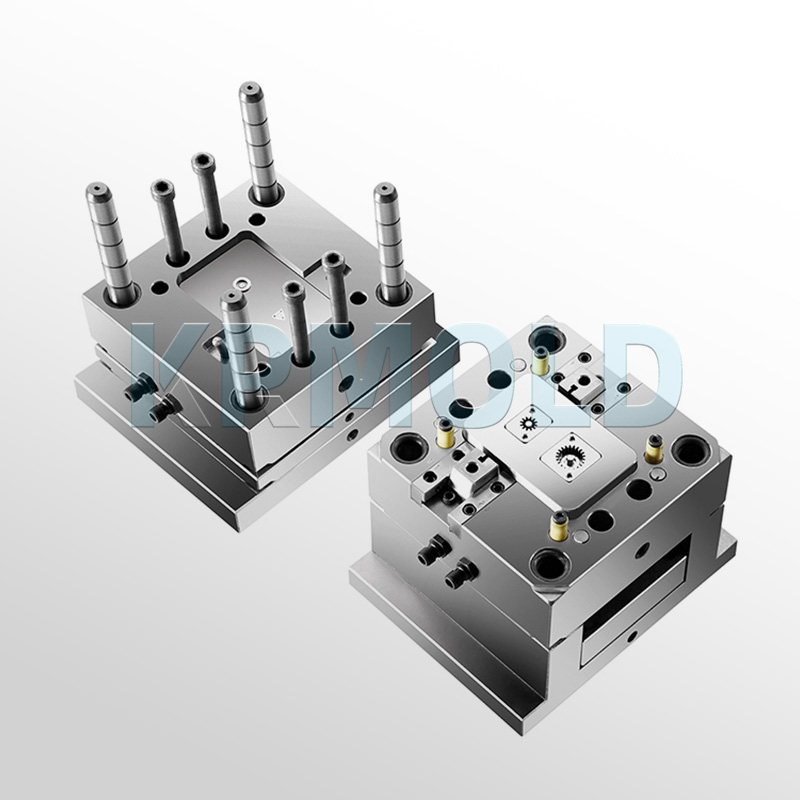
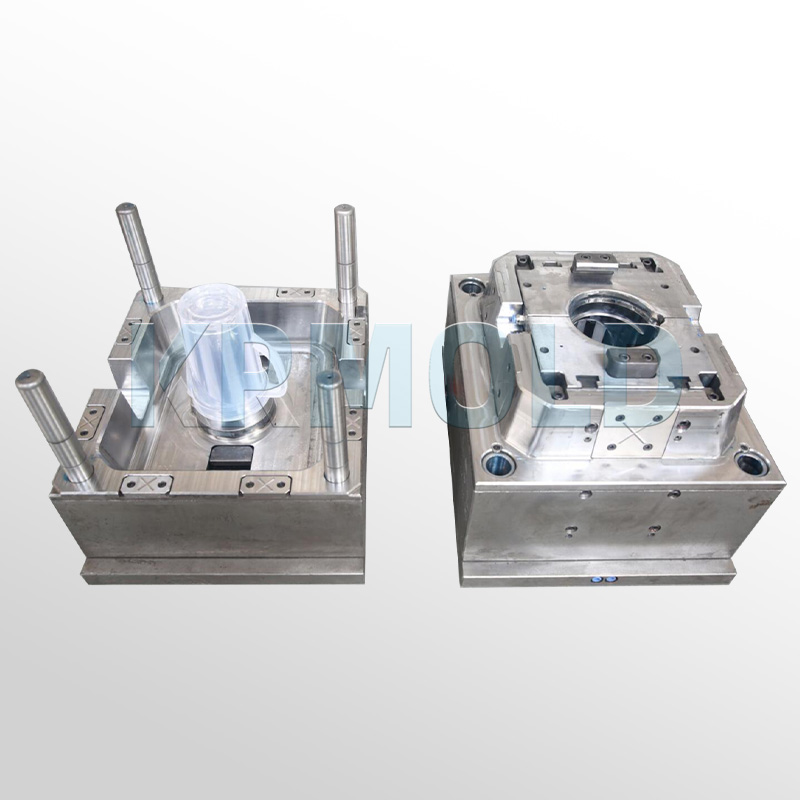
+86-13702855825Car dashboard injection molding is a manufacturing process that produces parts by injecting molten material into automotive interior trim molds. This process occupies an important position in industrial production and is widely used in various industries. High-precision dashboard molds on the market are often made of hardened steel, pre-hardened steel, aluminum or beryllium copper alloy. There are significant differences in cost, wear resistance and service life of these injection molds of different materials, so customers can choose the appropriate automotive interior trim molds according to actual production needs.
| 1 | Injection Molding Process and Workflow of Automotive Interior Trim Molds |
| 2 | Injected Plastic Materials |
1. Injection Molding Process and Workflow of Automotive Interior Trim Molds
The workflow of car dashboard injection molding can be divided into several main steps, each of which is crucial to ensure the quality and precision of the final product.
(1) Locking
In the first step of car dashboard injection molding, the high-precision dashboard molds need to be locked. The purpose of locking is to ensure that the automotive interior trim molds remain tightly closed during the injection process to prevent the molten plastic from leaking out during injection. The clamping device is usually driven by a hydraulic system to tightly combine the two halves of the high-precision dashboard molds by applying a certain amount of pressure. The locking force of the automotive interior trim molds needs to match the pressure generated during the injection process to ensure the stability of the car dashboard injection mold throughout the injection process.
(2) Injection
Once the automotive interior trim molds are locked, the next step is to inject the molten plastic into the high-precision dashboard molds. In this process, the plastic particles are first heated to a molten state and then injected into the automotive interior trim molds cavity through a syringe. Injection speed, pressure and time are key factors affecting product quality. In this step, the design and structure of the car dashboard injection mold will directly affect the fluidity of the molten plastic, thereby affecting the precision and appearance of the final product.
(3) Holding pressure
After the injection is completed, a certain pressure will appear inside the high-precision dashboard molds. This stage is called holding pressure. The purpose of holding pressure is to replenish the plastic that shrinks due to cooling, ensure that the plastic in the automotive interior trim molds cavity is completely filled, and avoid the generation of voids and defects. The setting of holding pressure time and pressure needs to be optimized according to the specific plastic material and product requirements to achieve the best molding effect.

(4) Cooling
After the holding pressure is over, the plastic inside the high-precision dashboard molds needs to be cooled to solidify and car dashboard injection mold. The length of the cooling time directly affects the production cycle and quality of the product. The cooling system usually consists of water cooling or air cooling, which controls the temperature of the high-precision dashboard molds to ensure that the plastic reaches the best hardness and strength within a reasonable time. During the cooling process, the temperature control of the car dashboard injection mold is very critical. Too high or too low temperature will affect the performance of the final product.
(5) Mold opening
After cooling is completed, the high-precision dashboard molds will be opened. This process requires ensuring smooth opening and closing of the car dashboard injection mold to avoid damage to the automotive interior trim molds due to jamming. When opening the car dashboard injection mold, mechanical devices are usually equipped to assist in opening to reduce the risk of manual operation. After the high-precision dashboard molds are opened, the product will be in half of the car dashboard injection mold and needs to be prepared for subsequent removal.
(6) Product removal
The last step is to remove the molded product from the automotive interior trim molds. This process can also be completed using a robotic arm or other auxiliary equipment to improve efficiency and safety. The removed product needs to be inspected and cleaned to ensure that there is no residual plastic and impurities. At this point, the product may require further post-processing, such as deburring, surface treatment, etc., to meet the final use requirements.
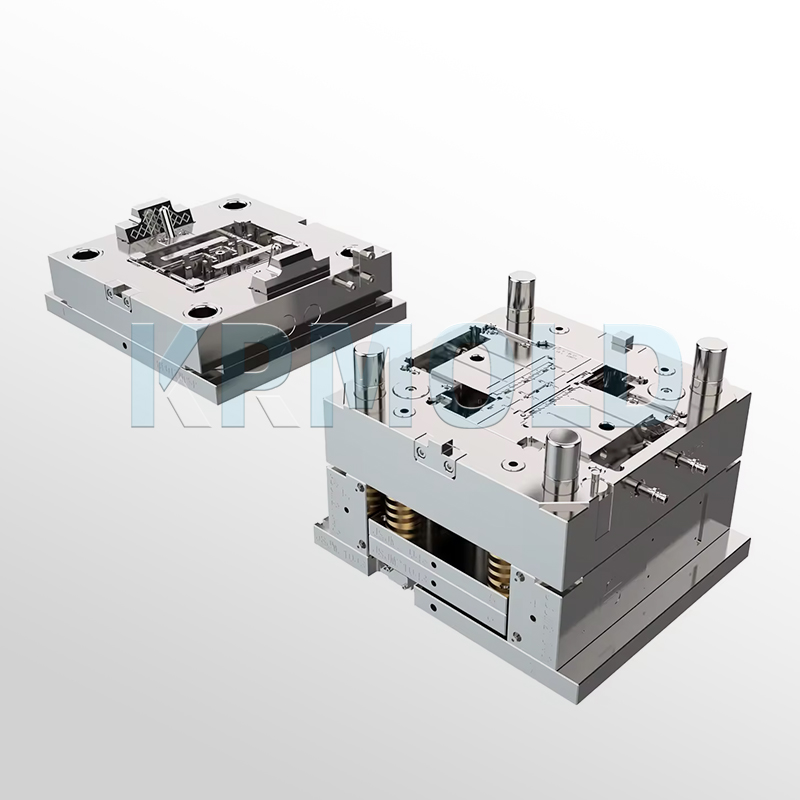
2. Injected Plastic Materials
In automotive interior trim molds, there are many types of injected plastic materials, among which high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE) are the most commonly used. The following are some common plastic materials and their uses:
(1) High-density polyethylene (HDPE)
HDPE is a high-strength, chemical-resistant plastic that is widely used in the manufacture of containers, pipes, and household items. Its advantages lie in its good toughness and impact resistance, making it suitable for products that need to withstand external forces.
(2) Low-density polyethylene (LDPE)
LDPE has good flexibility and transparency and is often used in the production of bags, films and packaging materials. Its advantage is that it is easy to process and suitable for large-scale production.
Polypropylene is a lightweight, heat-resistant plastic that is widely used in food packaging, automotive parts and home appliance housings. Its advantages are good chemical resistance and high melting temperature, making it suitable for high-temperature environments.


(4) Polystyrene (PS)
Polystyrene is an easy-to-process plastic that is often used to make disposable tableware, toys and electronic product housings. Its advantages are low cost and suitable for large-scale production.
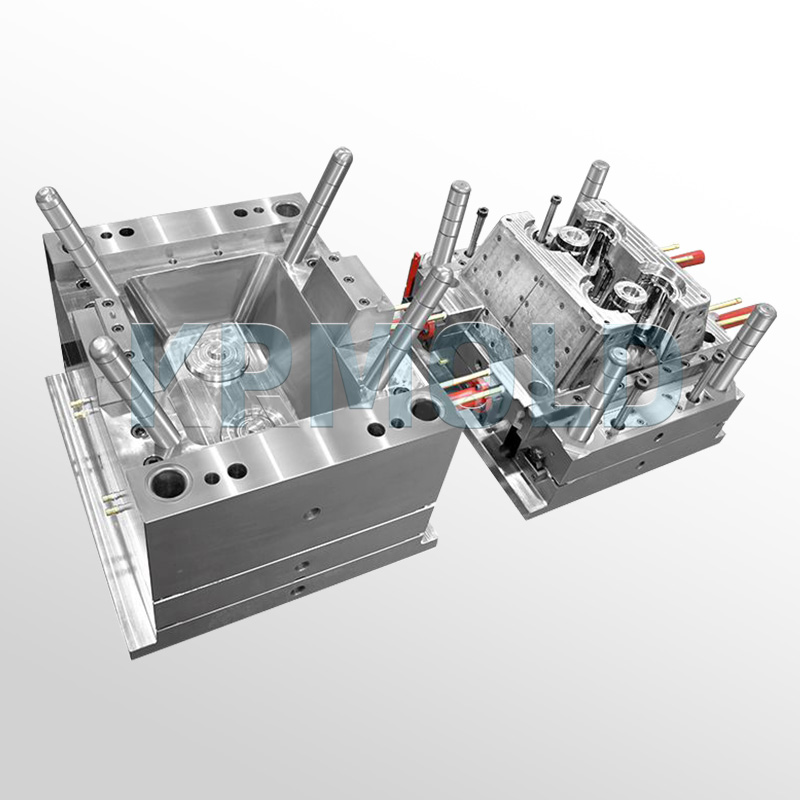
(5) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl chloride is a wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant plastic that is widely used in cable insulation, pipes and building materials. Its advantages are long service life and suitable for use in various environments.
Polycarbonate is a transparent and tough plastic that is often used to make optical lenses, electronic product housings, etc. Its advantage is that it has strong impact resistance and is suitable for products that require transparency and strength.


These plastic materials have their own characteristics, and choosing the right material is crucial to the quality and performance of injection molded products. When choosing automotive interior trim molds, customers should consider the characteristics and cost of the material based on the product's use requirements and environmental conditions to achieve the best results.