
KINGREAL UNIVERSAL IND., LTD
Phone
+86-13702855825| 1 | Principle of Gas-Assisted Injection Molding |
| 2 | Factors Affecting Gas-assisted Injection Molding Prices |
Gas-assisted injection molding is particularly effective in saving material for tubular and rod-shaped parts, such as handlebars, seat armrests, window frames, and imitation wood furniture.
The material savings for these parts can reach as high as 20%-40%. For large flat parts, such as door panels, refrigerator trays, and automotive interior and exterior trim, the use of gas-assisted reinforcement can eliminate warping caused by residual stress and improve part strength.
Furthermore, home appliances are one of the largest applications for gas assist injection molding technology. Over 90% of large-screen color TVs over 64cm on the market utilize gas-assisted injection molding.
With the growing market demand for large-screen color TVs and sedans, and the increasing popularity of home computers, the application of gas assist injection molding in home appliances is poised to generate immeasurable economic benefits.
Many people wonder how much gas-assisted injection molding costs. This article will provide a detailed explanation. |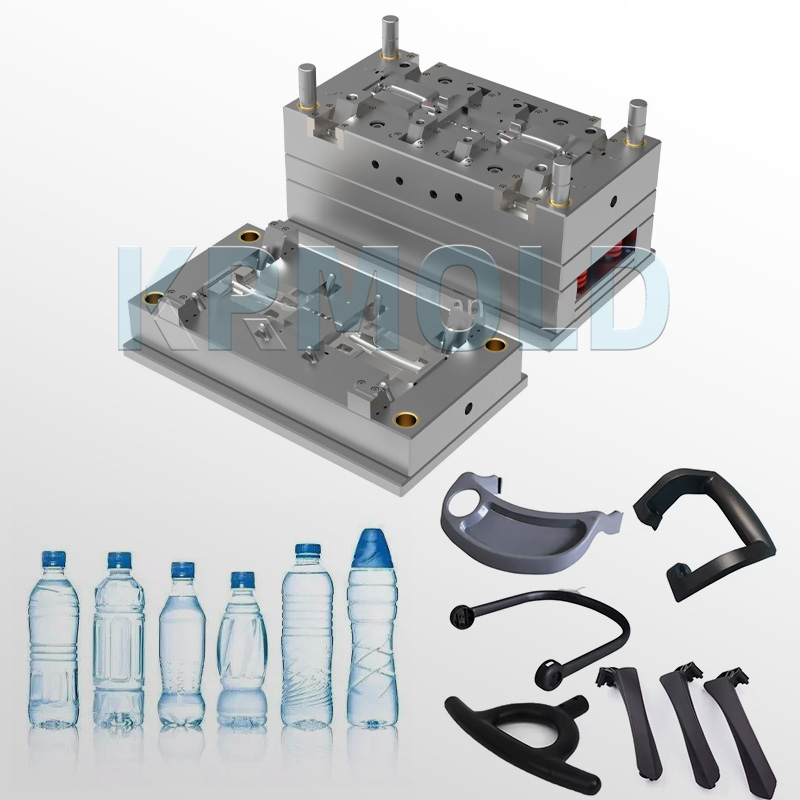  |
1/ Principle of Gas-Assisted Injection Molding
A gas assist injection molding system injects an inert gas (usually nitrogen) directly into the plasticized plastic in the mold cavity via a segmented pressure control system. This causes the interior of the part to expand, creating a hollow space while maintaining the product's surface appearance.
Gas-assisted injection molding can be considered a variation of blow molding. The process begins by injecting a precisely measured amount of molten plastic into the mold cavity, a process known as "underfilling." A specific volume and pressure of high-pressure nitrogen is then injected directly into the molten plastic. Surrounded by the molten plastic, the gas diffuses along the path of least resistance.
Because the plastic temperature near the mold wall is low and its surface viscosity is high, while the molten plastic in the thicker part is hotter and has a lower viscosity, gas easily penetrates and displaces the molten plastic in the center, forming air channels in the thicker part.
The molten plastic displaced by the gas is then pushed toward the mold end by the gas pressure until it fills the mold cavity. During the cooling phase, the compressed gas maintains pressure and compensates for shrinkage in the molten plastic. After the part cools and solidifies, the gas is released, and the mold is opened and ejected.
2/ Factors Affecting Gas-assisted Injection Molding Prices
(1)Gas-assisted Injection Mold Cost
Once the gas-assisted injection mold cost is determined, it remains a fixed cost throughout the mold's lifespan, without any intermediate modifications. That is, regardless of the number of parts molded, the mold cost per part decreases. Therefore, the greater the volume of molded parts, the lower the mold cost per part.
a. Mold Design Cost
Design cost also includes the costs incurred during the initial communication phase. Design work primarily includes Design for Manufacturing (DFM) analysis, Computer Aided Design (CAE) analysis (for complex parts), mold structure design, 2D drawing output, and subsequent programming. Typically, design costs account for 5-10% of the total mold cost.
b. Mold Material Cost
Raw material costs include the steel for the fixed and movable molds, auxiliary systems, standard parts, and the mold base. They typically account for 30-40% of the mold cost, with the approximate contributions of each component as follows:
Standard parts 10%, auxiliary systems 20%, core 40%, mold base 30%
c. Mold Processing Cost
Gas-assisted injection mold processing costs include the costs of all steps involved in mold processing, including machining, EDM, wire cutting, grinding, as well as heat treatment, polishing, assembly, and trial molds. Because the mold body is a single-piece product, manufacturing costs account for a high proportion of the total mold cost, typically reaching 40-50%.
A mold primarily consists of the mold base and the molded parts. The mold base is typically purchased from outside and involves minimal processing. Mold processing primarily focuses on the molded parts (cavity, core, lifter, slider, insert, etc.). The following processing methods are typically used to process the molded parts.
General processing includes CNC machining, wire cutting, deep hole drilling, EDM, polishing, graining, lapping, benchwork, and heat treatment.

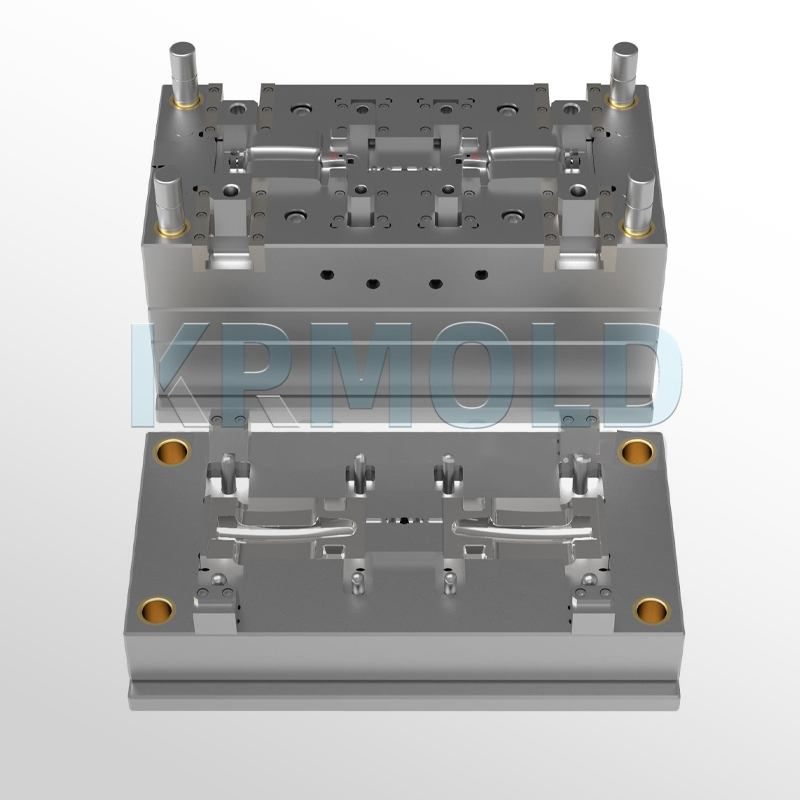
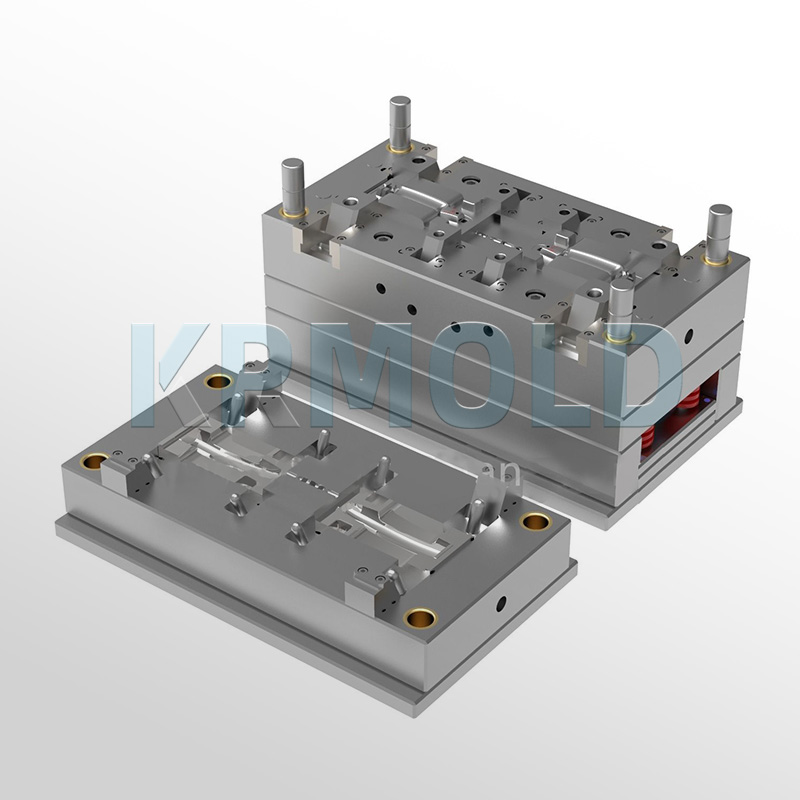
(2)Gas Assist Injection Molding Machine Cost
The gas assist injection molding cost here refers to the direct costs incurred during the production and processing of injection molded parts, specifically the gas-assisted injection molding costs, which primarily include:
a. Labor Cost: The production of injection molded parts requires workers to operate the machines. In some non-automated injection molding processes, manual labor is also required for sprue trimming, visual inspection, and packaging. These worker wages are included in the gas-assisted injection molding cost.
b. Electricity Cost: The operation of the gas assist injection molding machine and auxiliary equipment consumes electricity. The higher the equipment power, the greater the electricity consumption.
c. Equipment Depreciation Cost: The production of injection molded parts requires the use of gas-assisted injection molding machines, auxiliary equipment, and other equipment. Equipment depreciation is essential. The formula for calculating equipment depreciation cost is:
Equipment Depreciation Cost = Original Equipment Price / Estimated Equipment Lifespan
Labor costs, electricity costs, and machine depreciation account for the largest portion of machine costs. Within the same brand of gas assist injection molding machine, the larger the tonnage, the higher the electricity costs, machine depreciation, and maintenance costs. Machine costs also vary between different brands, even for the same tonnage.
gas assist injection molding cost = machine cost × molding cycle time.
The gas-assisted injection molding cycle time is influenced by many factors, such as filling time, holding time, dissolution time, and mold opening and closing time. However, cooling time is the most significant and influential factor.
The above introduces the factors that affect the price of gas-assisted injection molding. If you need more information or want to know how to reduce the price of gas assist injection molding, please contact KRMOLD.